Configuration Management Databases: Adding value for partners and their customers
Barry Turner
Senior Consultant, ISSI
Configuration management is a core discipline of IT service management that enables planning, incident management, and asset and risk management. A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) is one approach to configuration management that started in the 1980s as a concept with ITIL. To quote ITIL, "A configuration management database (CMDB) is an ITIL term for a database used by an organization to store information about hardware and software assets (commonly referred to as configuration items)."
The key to implementing an effective CMDB is having accurate information. In the rapidly changing cloud world, information on every configuration item must be automatically and frequently updated. This can be done in real time, although it is more commonly done once a day, either overnight or in a low-demand period.
The CMDB concept splits cloud partners into two broad groups: those that do, and those that don't. As with many aspects of cloud service management, there is no right or wrong way, simply the way that provides the most effective service to your customers. The objective of this blog is to help partners make fact-based decisions on a CMDB investment for cloud service delivery.
Why should you invest in a CMDB?
There are two primary reasons to invest in a CMDB:
- To improve the quality, security, and efficiency of service delivery.
- To become compliant with one or more of the vendor-managed service certifications or to achieve an external certification such as ISO20000:2019.
A CMDB is one approach to implementing configuration management. While working with the cloud partner community I've seen the following approaches to configuration management:
- Configuration management is limited to version control of infrastructure code releases and managed through a git repo with varying amounts of detail added as notes.
- Configuration management is shared across multiple tools and activities such as a git repo for version control of releases, a cloud cost-management application for asset management and reporting, and a monitoring application for detailed asset information.
- Configuration management is completed with a CMDB, either as a standalone piece of software or integral to the service management application. Typically, this is either a third-party application or in-house developed software. I'll go more into these options below.
- Configuration information is provided to the customer's CMDB/configuration management system via a federation process.
What are the benefits of operating a CMDB?
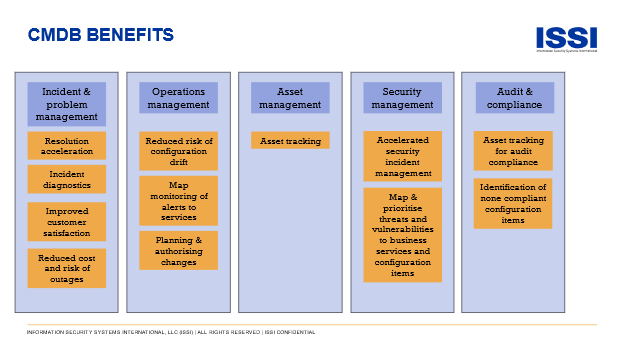
In a vendor audit in 2024, the partner operated a comprehensive CMDB and talked enthusiastically about the following benefits:
- Customer satisfaction: The CMDB enables the prevention of unnecessary incidents, improving service availability and the user experience.
- Employee satisfaction: Employees reduce the amount of time spent searching for information.
- Preventing incidents: Proactively preventing incidents is more efficient, such as ensuring upgrades are applied. There is also better visibility of potential problems.
- Single source of information on customer assets: This is critical for the sales team in activities such as driving contract renewals.
- Improved security: One example is the ability to quickly identify all assets affected by a security vulnerability or that need a new patch applied.
An additional benefit is audit compliance. Having an effective CMDB can reduce audit time and audit requirements for some third-party audits, such as PCI-DSS and ISO27001 audits.
The benefits are summarized in the illustration below:
How is CMDB and configuration management relevant to vendor audits
Configuration management or maintaining a CMDB are included in several of the cloud vendor audit programs that are provided by ISSI. The cloud vendors, however, take different approaches in their respective managed service provider audit checklists.
The respective MSP audit checklists for AWS and Google both mandate configuration management. Google specifies a CMDB, while AWS takes a broader view and requires the configuration management system to meet a set list of capabilities. Most of the other vendors, including Microsoft, HPE, and Oracle, have either configuration management or a CMDB as optional for an audit. This means the audit can be successfully completed without a CMDB or configuration management system.
ITILV4 / ISO20000:2019 relevance
Configuration management is a core concept within both ITIL V4 and ISO20000:2019 and is central to planning, operating, and maintaining services. However, neither ITIL nor ISO20000 now specify the use of a CMDB. The ITIL V4 foundation handbook talks about either using a CMDB or storing the configuration information in a range of data stores as described above. The ISO 20000-2:2019 document takes a similar approach, focusing on configuration management and stating that a CMDB is no longer mandatory and that other approaches can be used.
What are the challenges of a CMDB?
The key challenge with developing and maintaining a CMDB is accessing and maintaining information accuracy. A CMDB with inaccurate information is likely to create security vulnerabilities and extend incident fix times rather than the opposite.
For example, if an urgent security patch is issued for a specific version of Windows Server, poor-quality information in the CMDB could result in some servers not receiving the patch. According to Forrester's Modern Technology Operations Survey, 2022, over half of those surveyed do not trust their CMDB.
What Types of CMDB are available?
There are a variety of approaches to developing a CMDB, including:
- Dedicated software, either from an open-source provider or a dedicated software provider. Examples of these include Device42, a specialist CMDB software vendor, and i-doit, an open-source CMDB provider.
- IT Service Management applications and Professional Service Automation platforms such as Freshservice, ServiceNow, and ConnectWise typically either have a CMDB function or will integrate with a third-party product such as Device42.
- Build the software in-house. I have worked with several partners who have designed and built an in-house CMDB because they believed this was the most cost-effective option.
- Cloud Management Platforms such as Morpheus Data will integrate with third-party CMDB applications such as ServiceNow.
Is a CMDB relevant to my company and the level of required investment?
Here are the questions to ask to assess what approach to configuration management:
- What is the business objective that needs to be achieved?
- What compliance requirements exist, such as ISO 20000:2019 compliance or a vendor audit program?
- What currently exists that can be used to develop either a configuration management system or that can easily be extended, such as adding a CMDB function to the IT Service management application?
- What benefits will be generated from the operation of a configuration management system or CMDB?
- What are the risks involved in operating a configuration management system or CMDB? And what are the risks of not having either a configuration management system or CMDB?
- What investment and resources will be required to develop and maintain the capability and is this readily available?
- How will improved configuration management impact the customers?
Conclusion
If your business does not operate a Configuration Management Database solution, implementing one may require time and money. However, in my experience, both partners and their customers benefit over the long term with a CMDB in place.
If you'd like more information about how ISSI can help you with this decision or complying with audits that include CMDB features, contact ISSI at sales@issi-inc.com.
The author: Barry Turner is a Senior Consultant at ISSI and has worked with a broad range of cloud partners and vendors since 2015. He has 27 years of service creation experience working with telecommunication and cloud service providers across EMEA on behalf of ISSI, Microsoft, Cisco, Mitel & Agile Programs. He currently holds ITIL V4 Foundation, Customer Success Manager Level 2, ISO27001:2013 lead auditor certifications, and is PMP certified.
ISSI: As a leading consulting firm partnering closely with top cloud technology companies, ISSI is uniquely positioned to guide you through your cloud partner transformation journey. Let us help you unlock the full potential of this opportunity. Contact us today to begin your transformation. For more information, contact us at: sales@issi-inc.com.
References
Additional Articles
Developing the right service portfolio for your business
Ram Singlacher, Senior Consultant, ISSIDeveloping the Right Service Portfolio for Your Business By Ram Singlacher, Senior Consultant, ISSI One of the most vexing problems for partners working in the
The ways that partners can make money
Barry Turner, Senior Consultant, ISSIThe Ways That Partners Can Make Money By Barry Turner - Senior Consultant, ISSI One of the questions that ISSI hears from the cloud vendors
The Value of Service Processes for Cloud Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
Barry Turner, Senior Consultant, ISSIISSI works with partners across a spectrum of business models who want to become cloud-managed service providers. Within that ecosystem are two types of partners who can face a stumbling block on the way to becoming MSPs: cloud native partners and resellers.
- 15 DEC 2023
Monetization in customer success – Reality or Myth
Jonathan Lee, ISSI Customer Success Practice LeadMonetization in Customer Success – Reality or Myth By Jonathan Lee – ISSI Customer Success Practice Lead Customer Success Practice Blog Series #6 In my
06 JAN 2025ISSI AI Audits
Jamie Thordsen, Director of Partner Programs, ISSIOver the past two years the cloud industry has experienced a revolution in artificial intelligence as features and functionality such as generative AI spur enormous innovation and opportunities. ISSI has followed a parallel trajectory with our artificial intelligence domain expertise and offerings.
29 MAY 2025Developing a CA Score to Identify Your Best Customer Advocates
Jonathan Lee, ISSI Customer Success Practice LeadCustomer advocacy is the act of building and nurturing relationships with loyal customers, who then act as spokespeople and champions for your brand, products, or services. This process starts by identifying who those loyal customers are. To pinpoint your customer advocates, look for happy customers who frequently use your products or services in innovative ways and see a big impact on their business as a result.
